In the modern world, the stability and resilience of the banking system are crucial to the overall health of the economy. However, recent indicators suggest that the banking system may be on the verge of a systemic implosion. This potential crisis has raised concerns among policymakers, financial experts, and the general public alike.
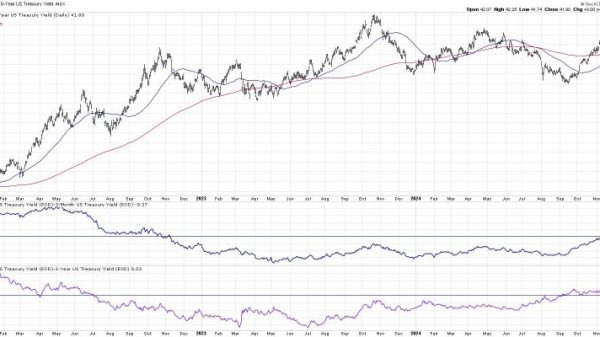
One of the key indicators that point towards a potential systemic implosion is the rising levels of non-performing loans within the banking sector. Non-performing loans are those loans where the borrower has failed to make interest or principal repayments for a certain period. A high level of non-performing loans suggests that the banking system is facing difficulties in recovering its funds, which can weaken the financial health of banks and lead to a domino effect across the sector.
Another critical factor to consider is the level of leverage within the banking system. Leverage, which is a measure of a bank’s assets to its capital, indicates the extent to which a bank is relying on borrowed funds to finance its operations. High levels of leverage can amplify the impact of any adverse economic shocks, potentially leading to a rapid deterioration in a bank’s financial position and, subsequently, to a systemic crisis.
Furthermore, the interconnectedness of banks through various financial instruments such as derivatives and interbank lending can exacerbate systemic risks. If one bank faces financial distress, it can trigger a chain reaction of defaults and liquidity shortages across the banking system. This interconnectedness can create a scenario where the failure of a single institution has the potential to destabilize the entire system.
Additionally, the emergence of new technologies and digital currencies poses challenges to the traditional banking system. The rise of fintech companies and digital payment platforms has disrupted the banking landscape, leading to increased competition and changing consumer preferences. Traditional banks that fail to adapt to these technological advancements risk losing market share and revenue streams, which can further weaken their financial position and contribute to a systemic crisis.
In light of these risks, it is essential for regulators and policymakers to closely monitor the health of the banking system and proactively address any emerging vulnerabilities. Strengthening regulatory oversight, enhancing risk management practices, and promoting transparency and accountability within the banking sector are crucial steps to mitigate systemic risks and safeguard financial stability.
Ultimately, the potential for a systemic implosion in the banking system underscores the importance of a resilient and well-regulated financial sector. By addressing the underlying vulnerabilities and implementing proactive measures, policymakers can help ensure the stability and integrity of the banking system, thereby safeguarding the broader economy from the devastating consequences of a systemic crisis.